The Effects of Social Isolation on Mental Health
Humans are inherently social beings, and a lack of support and interaction with others can lead to feelings of loneliness, cognitive decline, anxiety, and depression.
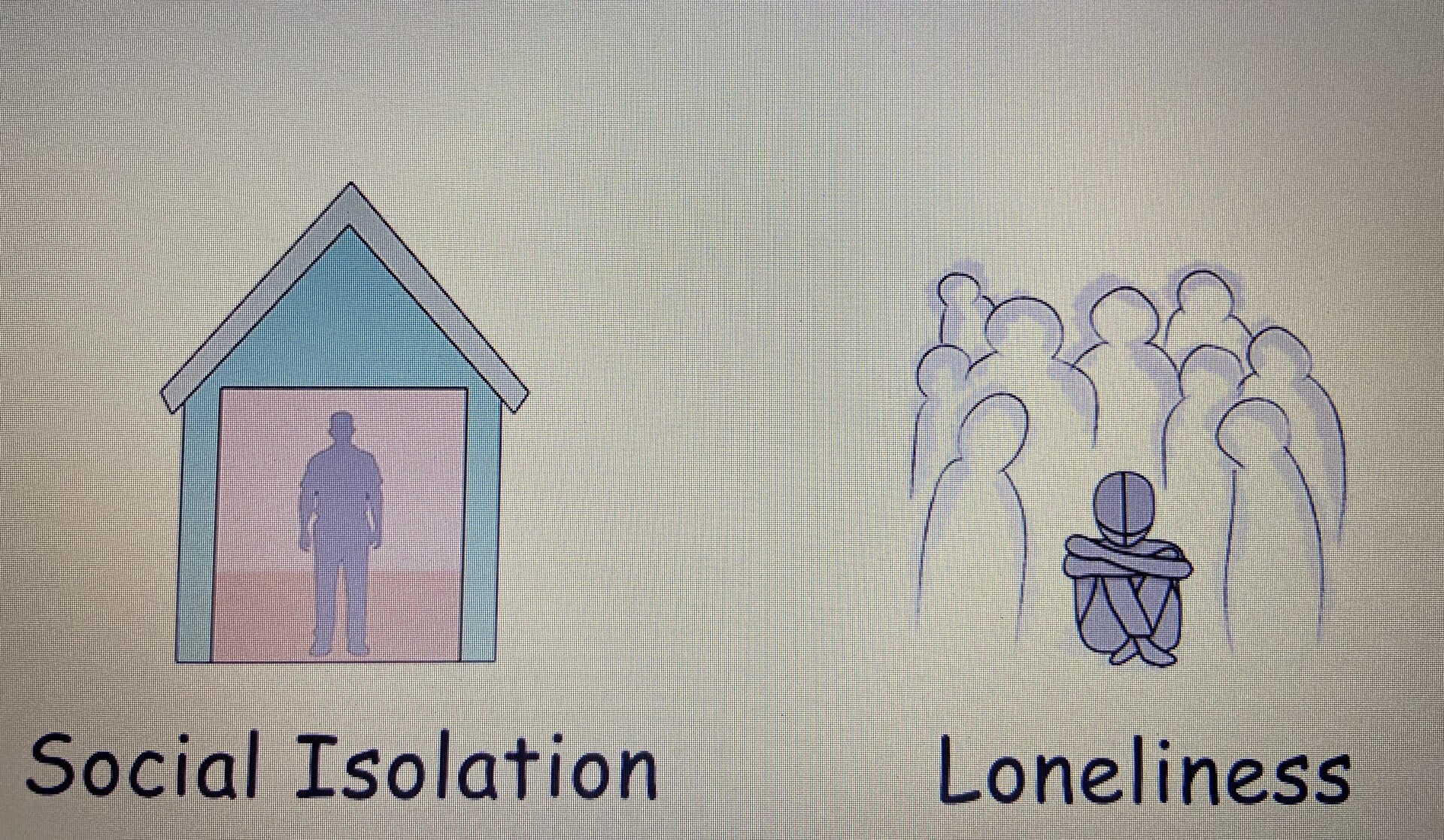
Social isolation involves being cut off from contact with others. This can involve physical isolation but also refer to feeling emotionally disconnected from social interaction.
People can become socially isolated both intentionally and unintentionally. While levels of social contact can vary over time, extended periods of social isolation can harm mental and physical well-being.
Isolation has also been connected to a greater risk for medical conditions such as heart disease, high blood pressure, weakened immunity, and reduced overall longevity.
Social isolation and mental health have a bidirectional relationship. Isolation can also lead to changes in the brain that might contribute to the onset of mental health conditions. Poor social support can make it more challenging for people to manage stress, which can also significantly affect health and well-being.
Meanwhile, social interaction and support can help people manage symptoms of stress, anxiety, depression, and other mental health challenges. Connecting with others and spending time together can foster a sense of belonging.
Reasons for Social Isolation
Social isolation can sometimes result from clear and immediate causes, like divorce or illness. In other instances, it develops gradually and may signal underlying issues in a person’s life.
In reality, social isolation is often influenced by a variety of factors, including:
- Depression
- Illness
- Social anxiety
- Stress
- Trauma
Depression
Social isolation frequently accompanies depression. Individuals with depression often experience symptoms such as low mood, disinterest, fatigue, hopelessness, and a lack of motivation, all of which can hinder their ability to maintain social relationships.
Illness
Chronic health conditions can also lead to social isolation. These conditions may impact mobility, making it challenging to participate in social activities. Additionally, stigma or feelings of shame can cause individuals with health issues to withdraw from social interactions.
Social Anxiety
Social anxiety leads individuals to experience intense fear in social situations. Those with this type of anxiety often cope by avoiding social interactions, which can significantly restrict their ability to sustain relationships and maintain social connections.
Stress
Major life stressors frequently lead to social isolation. For instance, divorce often results in the loss of social connections and may cause individuals to withdraw.
Similarly, the death of a spouse, financial difficulties, job loss, and retirement can all impact a person’s social engagement.
The COVID-19 pandemic was a particularly stressful event that heightened social isolation across all age groups globally. Measures such as social distancing, quarantines, and remote work disconnected many individuals from their usual sources of social interaction and support.
Even stressors typically viewed as “positive,” such as starting college or getting married, can lead to major life changes that disrupt a person’s social functioning.
Trauma
It is common for individuals who have undergone a traumatic event to isolate themselves as a coping mechanism.
Depending on the trauma’s nature, some people may find it difficult to trust others and fear being hurt again. Those with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) may also avoid social activities that could trigger memories of the traumatic event.


















